Dr. George HK Lau (Asso. Professor & Programme Leader (Testing & Certification), School of Science and Technology, OUHK) and I attended the seminar.
In the beginning, Mr. Johann Wong (Deputy Commissioner for Innovation and Technology, ITC, HKSAR Government) gave welcoming Remarks. He welcomed all guest and participants and explained the aims of the seminar to raise the public awareness on quality infrastructure in Hong Kong.
Group photo of all guests
Mr. Wong Wang-wah (Executive Administrator, HKAS and PSIB, Innovation and Technology Commission, HKSAR Government) gave opening remarks. Firstly, he mentioned the actual celebration dates of WMD on 20 May, WAD on 9 June and WSD on 14 October, respectively. He said a sound quality infrastructure is the cornerstone of a reliable conformity assessment system. Metrology, accreditation and standardization were three pillars supporting this quality infrastructure.
The first speaker was Dr. Barry Inglis (President, International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM)) and his presentation entitled “Metrology – Is Role in Trade, Energy and Quality of Life”. Firstly, he introduced the global infrastructure included International Bodies/agencies (e.g. WHO, WTO), Documentary Standards Writers (e.g. ISO, IEC), Certification Bodies (e.g. IAF, PAC), National Regulators (e.g. FDA, FAA) and Accreditation Bodies (e.g. ILAC, APLAC).
Dr. Inglis said “Metrology is the science of measurement and its application – Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement, whatever the measurement uncertainty and field of application”. Role of Metrology in Trade included Fair trading, International acceptance of products and testing, Food safety, etc. Role of Metrology in Energy included Energy transformation (e.g. efficiency, renewables), Distribution & Trade (e.g. electricity, gas, oil), Qualitification of energy content, Environmental impact, etc. Role of Metrology in Quality of Life included Health and Safety, Impact of emerging technologies, Food safety, Environment, etc. Finally, Dr. Inglis concluded that Metrology played a major roles and measurement in terms of the SI provided the basis for credible and reproducible measurements.
The second speaker was Mr. Peter Unger (Chairman, International Accreditation Cooperation ILAC) and his topic named “The Role of Accreditation in the Provision of Energy – The Perspective of ILAC and IAF”. Mr. Unger briefed the objectives of IAF and ILAC that they aimed to maintain the arrangements and to expand coverage into new economies so as to act as a central ‘hub’ to harmonize conformity assessment best practice. (We had met Mr. Peter Unger in Science Park before. Detailed link is in reference)
Mr. Peter Unger introduced the structure of Accreditation which supported by government, consumers and users. Then he said the provision of energy was the theme because energy was essential to daily activities. The IAF and ILAC Arrangements were structured to build on existing and developing regional MLAs/MRAs established around the world. He concluded that IAF and ILAC commit to develop a harmonized global approach for accreditation practices to esure equal reliability of accredited services as so to support developing economies to establish their accreditation infrastructure.
Mr. Rob Steele was the third speaker and his presentation title was “How Standards Level the Playing Field”. He said the world needed a great standards and conformance infrastructure that was aligned to meet customer needs.
Then Mr. Steele introduced ISO Global System which had 162 national members. There were many ISO’s works in recent years and he pointed out those standards promoted innovation in business which was really important.
Mr. Steele explained the matching of Good Regulatory Practice and Good Standards Practice. Then he briefed different ISO working group for energy such as ISO/IEC JTC 2, ISO 500001, ISO/TC 22, etc. Finally, he concluded government should assist national involvement in International Standards on energy management to promote good energy management practices.
Q&A Session
One of interested questions was “Why UK don’t use SI unit? But they used non-metric measurement system such as pound (lb), gallon, etc.” It was a difficult question because of historical development of measurement in England.
Mr. Lee Wah-kwan, Dennis (Head of Laboratory, Standards and Calibration Laboratory (SCL), ITC, HKSAR Government) was the fourth speaker and his presentation named “The Past, Present and Future of the Physical Metrology Infrastructure of Hong Kong”. Firstly, he quoted Nobel Laureate – Steve Chu’s statement “Accurate measurement is at the heart of physics, and in my experience new physics begins at the next decimal place.”
Moreover, Mr. Lee told us there was the 30th anniversary of SCL and he briefed the history. The details of SCL history is showed in the following photos.
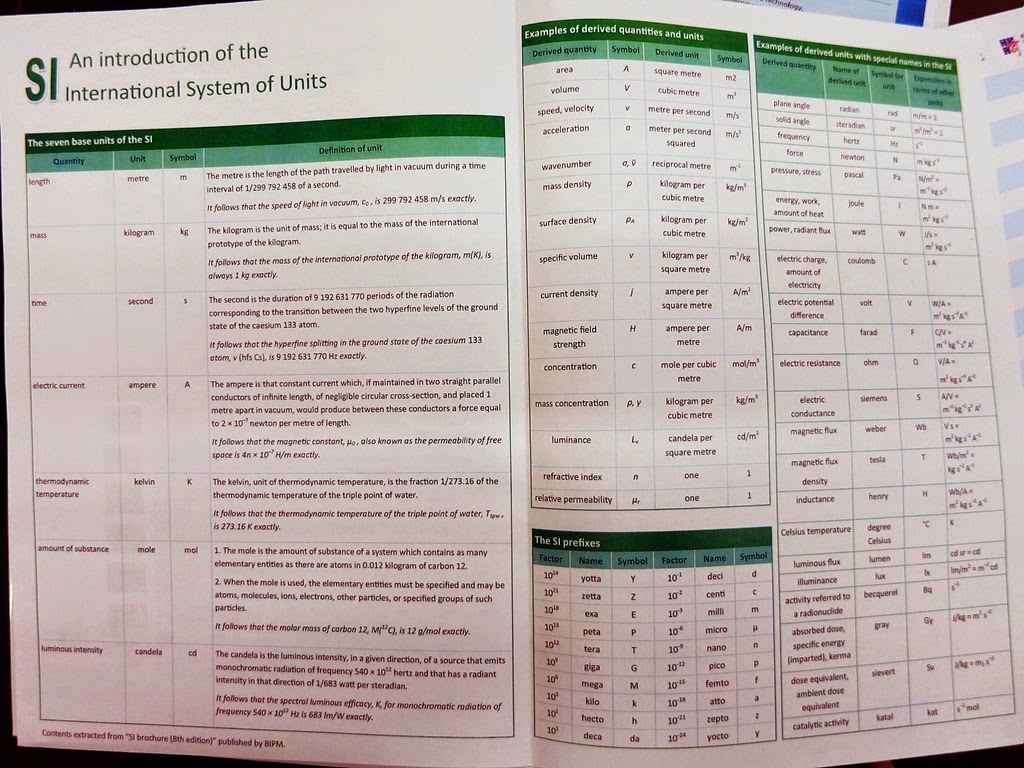
Mr. Lee also prepared a summary of International System of Units for each participants. Then He quoted Dr. Brian Bowsher (MD, NPL of UK) that “Metrology in the 2020s will play a key role in meeting the socio-economic and scientific challenges:
- A sustainable low-carbon economy
- Scientific discovery
- Innovation and R&D intensive growth
- The well-being and security of the citizen.”
At the end, Mr. Lee briefed the direction of developmental tasks in SCL were “Scientific and Industrial Metrology”, “Energy Related Metrology” and “Health Related Metrology”.
The fifth speaker was Dr. Della Sin (Assistant Government Chemist, GL, HKSAR Government) and her topic named “The Scientific Infrastructure of Assuring Measurement Quality”.
Firstly, Dr. Sin introduced the important pillars of Metrology, Accreditation and Standardization which caused reliable measurement results. The she introduced the Metrology-in-Chemistry activities included the Consultative Committee for Amount of Substance: metrology in chemistry (CCQM) level and the Regional Metrology Organization (RMO) level, Production of Certified Reference Materials (CRMs), Proficiency Testing Programmes, International and Regional Collaborations.
The following diagram showed recently comparison related to Energy in CCQM level and RMO level.
The last speaker was Mr. Harry Lai (Assistant Director, Electrical & Mechanical Services Department, HKSAR Government) and his presentation named “Energy Efficiency and Safety of Electrical Products in Hong Kong”. Mr. Lai introduced Energy Efficiency Labelling Schemes (EELS) and Electrical Products (Safety) Regulation.
For EELS, there were separated into Voluntary EELS (VEELS) and Mandatory EELS (MEELS). EELS aimed to provide information for consumers to select energy efficient appliances. The energy labels were shown below. Mr. Lai said MEELS achieved an energy saving of 175 million kWh per year (equivalent to reduce 122,000 tonnes of CO2 emission annually).
Finally, Mr. Lai concluded that the contribution of Standards and Accreditation to Energy Efficiency and Safety of Electrical Products included “Standards adaptation to minimize technical barriers” and “Accreditation on Testing Facilities which provided confidence test results”.
Q&A Session
I asked for advice if no reference standards in advance equipment (e.g. SAM, ToF-SIMS & XPS). Dr. Della Sin said they would do by themselves for calibration and verification.
Reference:
World Metrology Day 2013 Seminar - http://qualityalchemist.blogspot.hk/2013/05/world-metrology-day-2013-seminar.html
ILAC representative visit to HKSTPC Laboratories - http://qualityalchemist.blogspot.hk/2012/09/ilac-representative-visit-to-hkstpc.html
HKCTC – http://www.hkctc.gov.hk/en/about.html
SCL – http://www.itc.gov.hk/en/quality/scl/about.htm
GL – http://www.govtlab.gov.hk/english/home.htm
HKAS – http://www.hkas.gov.hk
PSIB – http://www.itc.gov.hk/en/quality/psis/
HKSQ – http://www.hksq.org/